Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate - Enables continuous wireless transmission between devices in a 1:1 pairing and uses a point-to-point system which makes it ideal for audio streaming. Some examples include: wireless headphones, wireless speakers, and in-car systems.
Bluetooth LE: Point-to-point - Enables short-burst wireless connections and uses multiple network topologies, including point-to-point topology for 1:1 device communications. Bluetooth LE p2p optimizes data transfers and is ideal for connected device products, such as fitness trackers and health monitors. Some examples include: sports and fitness equipment like FitBits, health and wellness equipment like toothbrushes and hospital equipment, and adaptations for your PC or phone like a keyboard or mouse.
Bluetooth LE: Broadcast - Enables short-burst wireless connections and uses multiple network topologies, including a broadcast topology for one-to-many (1:M) device communications. It supports localized information sharing and is well suited for beacon solutions, such point-of-interest information and item and wayfinding services. Some examples include: point-of-interest beacons like ones you find in stores to find deals or coupons on the shelves, item-finding beacons to find items like phones and wallets, and wayfinding beacons to help find your way around large areas.
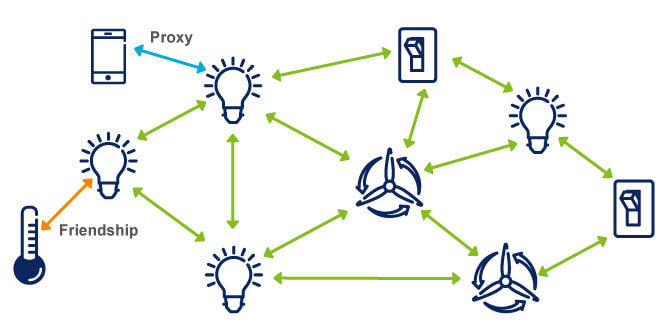
Bluetooth LE: Mesh - Enables short-burst wireless connections and supports multiple network topologies, including a mesh topology for establishing many-to-many (M:M) device connections It’s optimized for creating large-scale device networks and is ideally suited for building automation, sensor network and asset tracking solutions. Only mesh networking brings the proven, global interoperability and mature, trusted ecosystem associated with Bluetooth technology to the creation of industrial-grade device networks. Some examples include: building automation to make homes and offices a lot smarter by turning off multiple lights and having hundreds or even thousands of wireless devices to communicate reliably and securely, wireless sensor networks which are used in business to track certain devices and how they communicate with each other on the work floor, and asset tracking which is used to track many devices inside of a large building like a hospital or industrial complex.